Roles and Permissions
In default QuickAdminPanel generator, we generate two user roles - Administrator and Simple User. They both have the same permissions for all CRUDs and Modules, except for User Management which is available only for administrator.
The whole Permissions system is stored in the database in these DB tables:
permissions
roles
permission_role
role_user
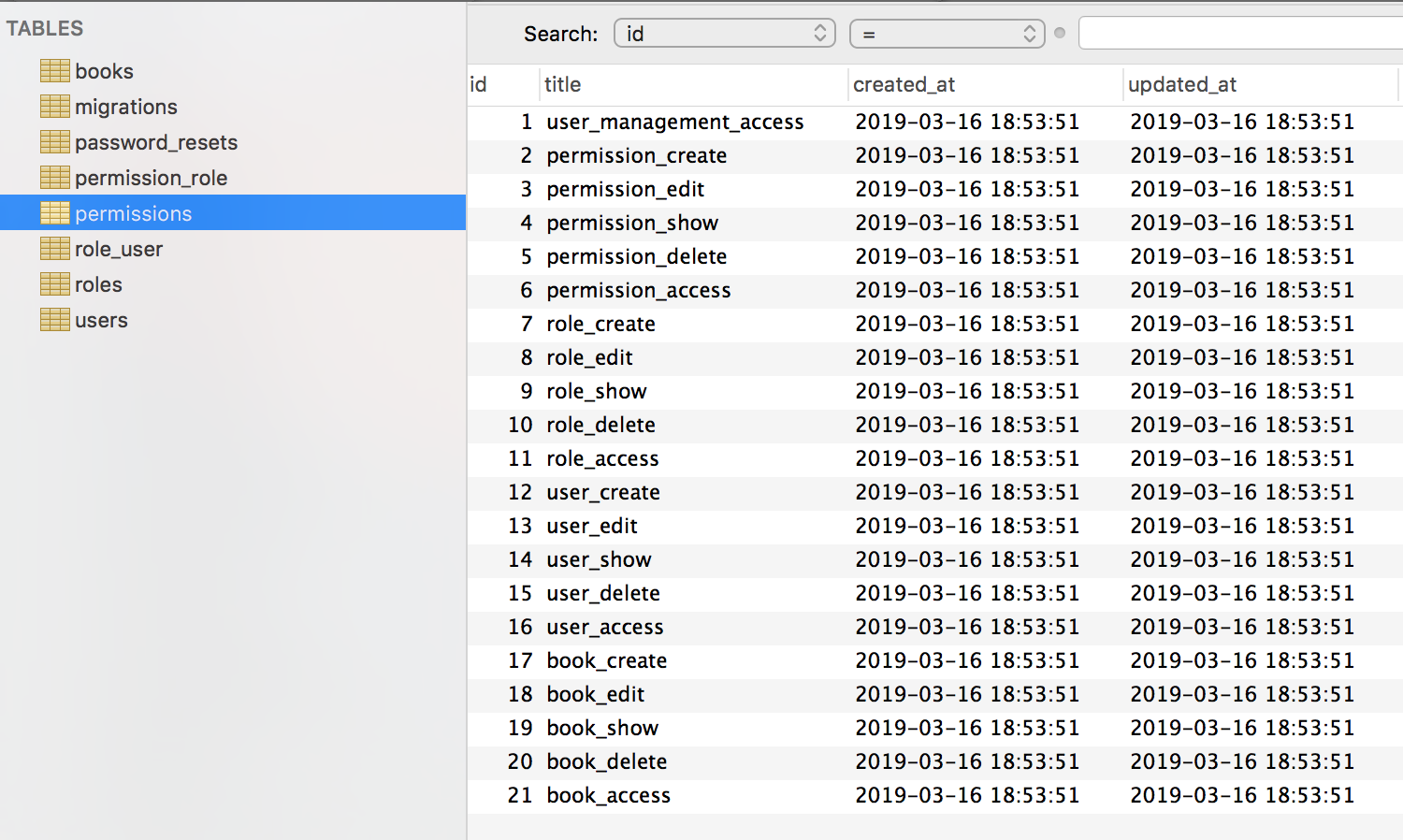
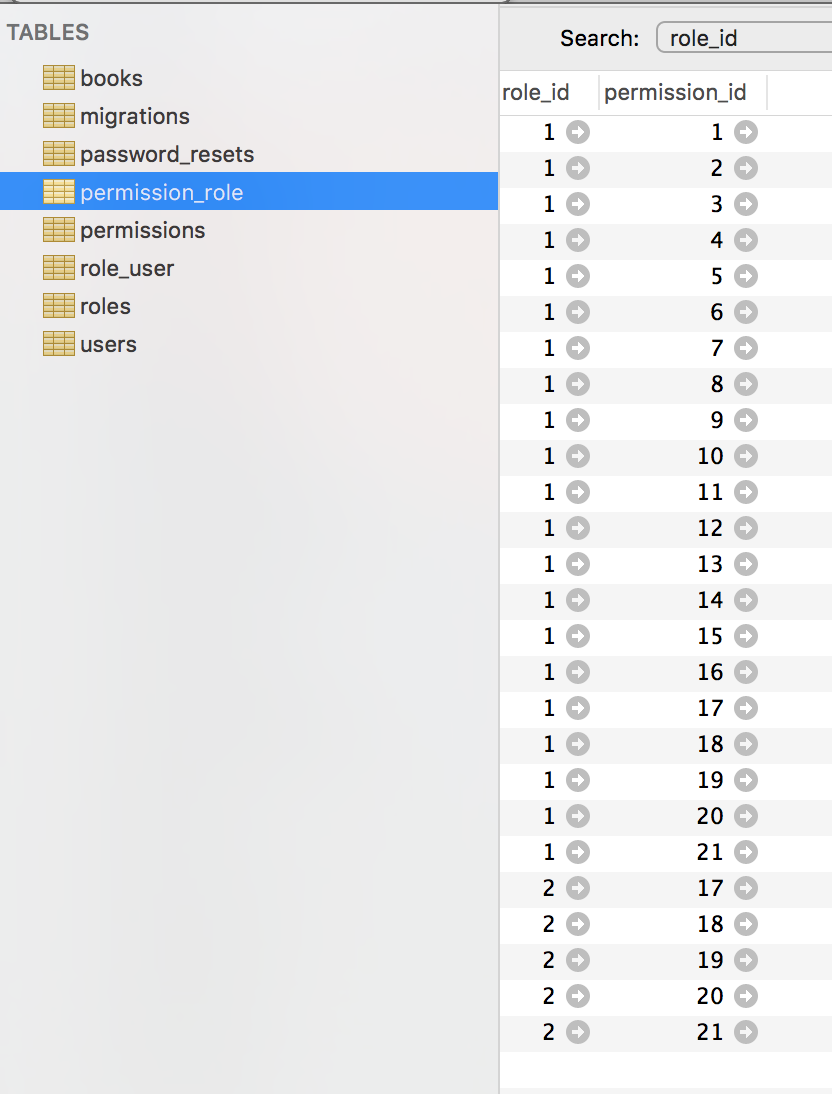
Every CRUD has five default permissions generated:
*_access (whether user sees menu item in sidebar)
*_create (whether user can access create form and add new record)
*_edit (whether user can access edit form and update existing record)
*_show (whether user can access "show" page of a record)
*_delete (whether user can delete records)
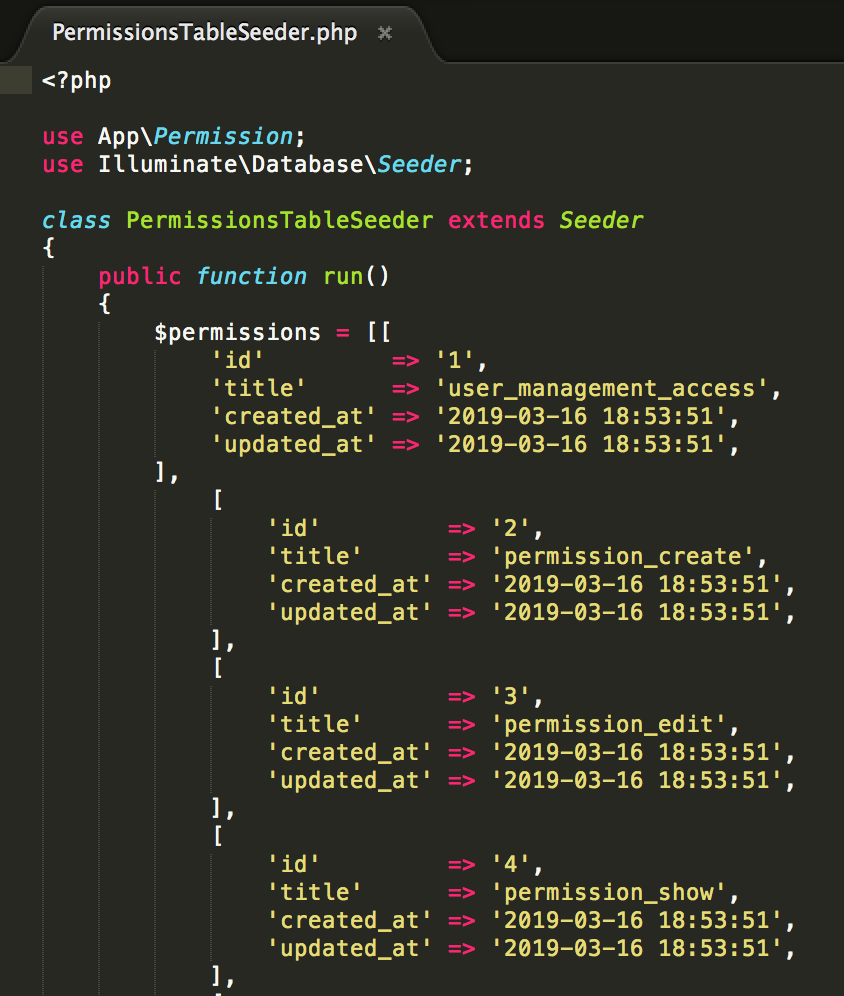
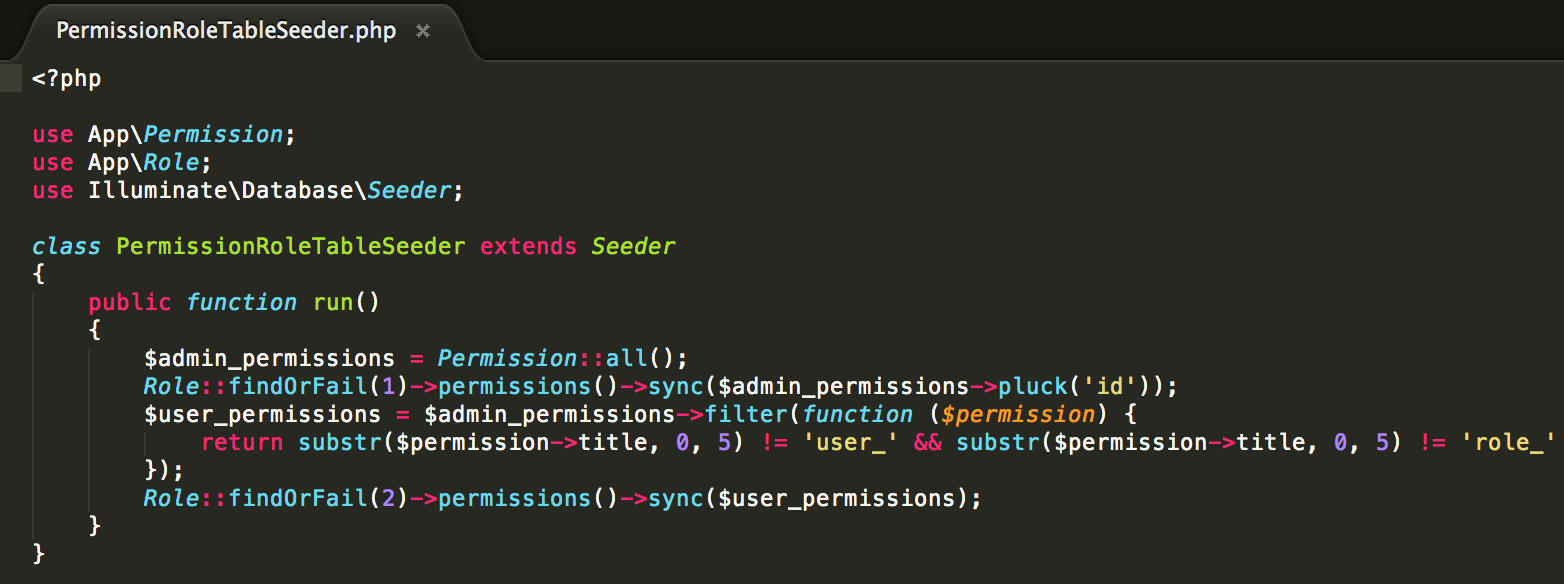
These records are seeded with Seeder files, see examples below:
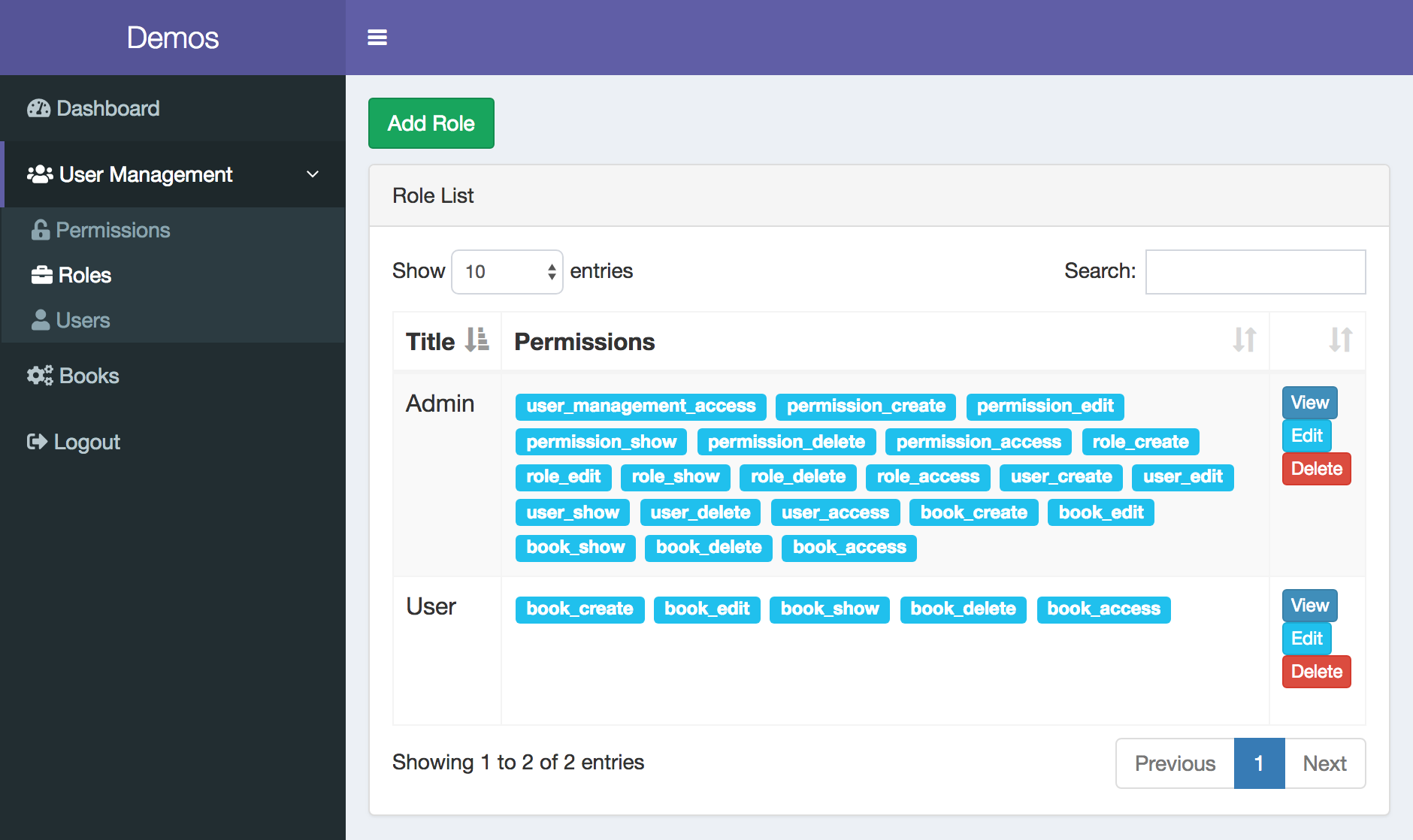
If you want to change permissions in downloaded panel, you can log in as Administrator user and go to menu item User Management -> Roles, and then assign all permissions you want to a particular role, by editing it.
In the generated code, we check the permissions in every method of Controller, see Gate and abort_unless() methods in example:
On top of that, we add a check in Form Request classes, see example:
For more information, how Gates work in Laravel, see official Laravel documentation.
Last updated